
Yaquina Bay Bridge Cathodic Protection Rehab wins ICRI Award of Excellence
Vector Corrosion Technologies Wins ICRI Award of Excellence for Cathodic Protection Work on the Hist…
On August 22, 2023, the Association of Materials Protection and Performance (AMPP) released an updated standard titled: NACE SP0216-2023 - Galvanic Cathodic Protection of Reinforcing Steel in Atmospherically Exposed Concrete Structures. These guidelines are intended for owners, engineers, architects, contractors, and those concerned with the mitigation of reinforced concrete corrosion through the application of galvanic cathodic protection (GCP) systems.
This new (updated) standard requires designers of GCP systems to consider the performance of the anodes over their designed service life.


As you see from the charts above, the output of galvanic systems follows an exponential decrease in current output similar to the 'half-life' principle, where the current is halved at constant periods of time. End-of-life performance is a critical criterion when designing and specifying a corrosion protection system, as it ensures the system will remain effective at mitigating corrosion for the entire duration.
Legacy GCP specifications tend to focus on the mass of zinc, but this is a gross oversimplification that overlooks other critical performance factors like:
Service Life expectations
Efficiency/Utilization Factor of the anode
Minimum current density delivered over the anode service life - This minimum level is governed by the corrosion risk level of the existing concrete or its environment.
Verify the following information for a product before specifying:
To help asset owners and engineers better identify their corrosion protection requirements, we have published sample performance-based specifications for various GCP systems on our technologies pages.

Vector Corrosion Technologies Wins ICRI Award of Excellence for Cathodic Protection Work on the Hist…
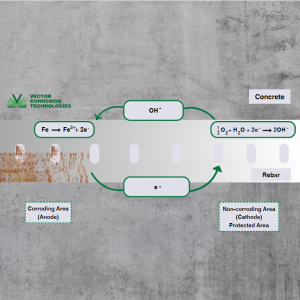
Why Does Corrosion Happen? : Understanding Corrosion of Steel in Concrete Structures : Welcome to …
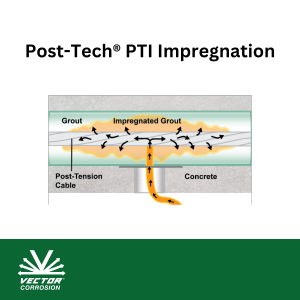
Post-tensioning (PT) tendons have been a staple of concrete design and innovation for many years. …